Introduction
Acute leukemias can be divided into acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Common presentations of acute leukemia include fever, symptoms of anemia, bleeding, bone pain palpable Lymph nodes or spleen and symptoms due inflation or leukocystasis. Extramedullary mass is rare and can be of myeloid tissue and known as Chloroma or myeloid (granulocytic) sarcoma which one of the WHO classifications for acute myeloid leukemia. Common sites of occurrence are skin, sinuses, bone and other. It's rarely involve central nervous system. Spinal cord involvement usually manifest as epidural mass causing cord compression. Spinal epidural tumor with acute leukemia and myeloid sarcoma is rare and can be found in 3-9% in patients with leukemia.
In this review we decide to review the cases of spinal cord compression caused by acute myeloid leukemia (including Chloroma) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia due to the significance of such presentation in addition to reports that Myeloid sarcoma of the spine has very poor prognosis
Methodology:
We have reviewed the literature using: PubMed, google scholar, Scopus for patient with spinal cord compression and acute leukemia. We used the search term and synonyms : : acute myeloid leukemia , acute myelocytic leukemia , acute monocytic leukemia , acute lymphoblastic leukemia , acute lymphoid leukemia, chloroma , myeloid sarcoma ,granulocytic sarcoma, spinal cord compression .We included adult patients above 18 years old only cases we exclude pediatrics cases and cases of chronic leukemia's and other myeloproliferative disorders as well as cases of central nervous system involvement other than spinal cord
Results
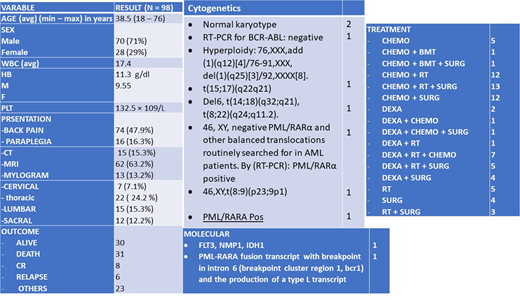
We gathered the information from 98 cases with general demographics, presentation, image modality, cytogenetics and molecular in addition to management and outcome.
We have found mean age for the patients is 38 years old with male predominance with 70% of the cases. The most presenting symptom was back pain in around 75% of the cases. Neurological findings showed sensory loss and parapreresis in most of the documented cases. MRI was most performed modality of imaging 63% followed by Computed tomography(CT) 15 % and then myelogram 13 %, which is least used due to invasive nature and before the era of MRI. The most common affected site on spinal cord were thoracic followed by lumbar. Cytogenetics and molecular data was not reported in most of the cases.
Patients were treated with either steroids or surgery or radiotherapy and or chemotherapy while few underwent bone marrow transplant, but the most common approach was surgery+ radiotherapy + chemotherapy combination. Steroids used in most of the cases especially in the cases of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and dexamethasone was the steroids of the choice mainly. The outcome of the patients were variable, 30 % were alive at the time of the reports 30 % died and 30 % between relapse and complete remission.
Conclusions
Acute leukemia can be presented as mass causing spinal cord compression which is very serious. There are is no standardized management of patients with acute leukemia who presented with spinal cord compression nether guidelines or steps to follow. Some reports speculated also specific morphology and cytogenetics association with predisposition to have Extramedullary mass, however there lack of reporting of such a valuable information. Large studies including all adjusted variables required to determine if spinal cord compression presentation can be an independent risk facto or not Effective diagnosis and prompt action should take place.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.